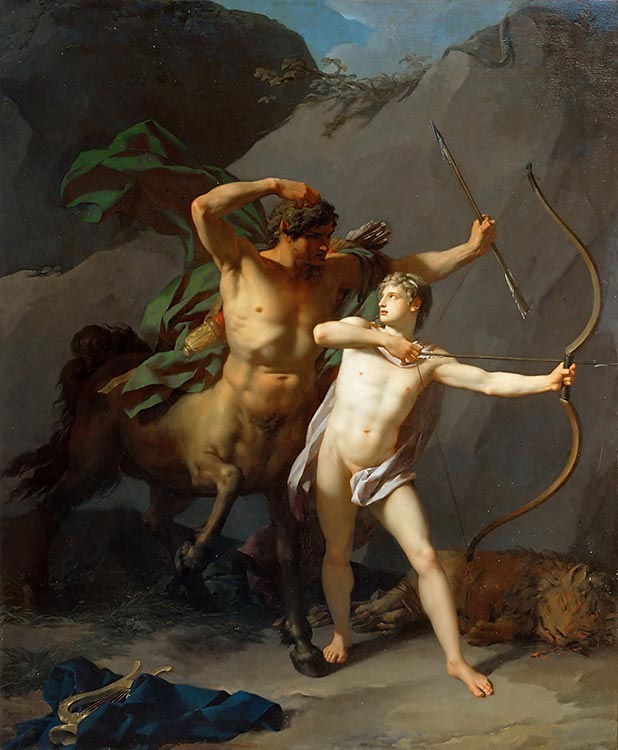

Achilles
The Greek hero Achilles was invulnerable excepting his famous weak heel, but a male shieldbearer broke through the warrior’s romantic defenses. While Homer never explicitly states a gay relationship between Achilles and sidekick Patroclus, many scholars read a romantic connection between the two, as only Patroclus ever drew out a compassionate side to the famously arrogant warrior. Patroclus’s death at the hands of Trojan Prince Hector sent Achilles into a rage in which he killed Hector and dragged his body around Troy. Other myths also disclose Achilles was struck by the beauty of Troilus, a Trojan prince.
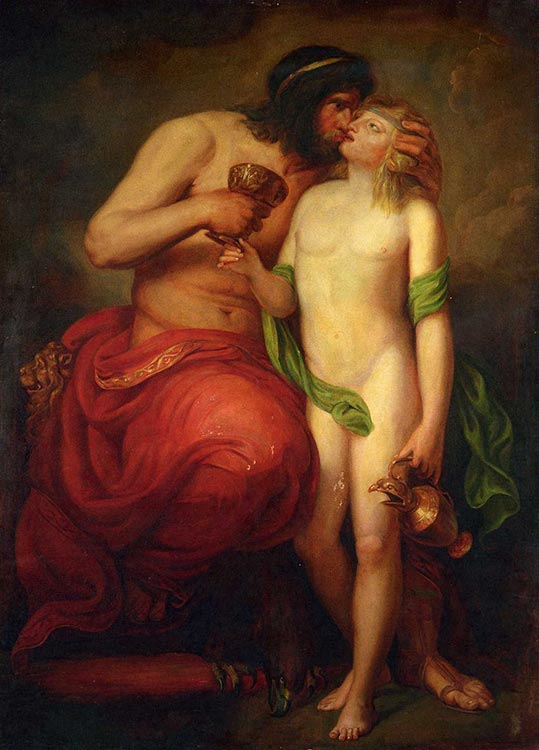

Zeus
While a famous philanderer who sired countless demigods by every peasant girl in need of an explanation to her parents, Zeus famously selected the young mortal Ganymede to serve as his cupbearer on Mount Olympus. The relationship provided the foundation of the custom of paiderastia, the practice of Greek men at the time maintaining erotic relationships with adolescent boys on the side.

Narcissus
A figure mostly known for his obsessive vanity, this son of a nymph and a river god would spend his last days gazing at his own reflection, but the first man he showed affection for was not himself. A myth traced in origin to the Boeotia region mentions a relationship between Narcissus and the smitten Ameinias, whom Narcissus would eventually grow tired of before sending him a sword as a kiss-off. Ameinias, desperately depressed over the rejection, killed himself.
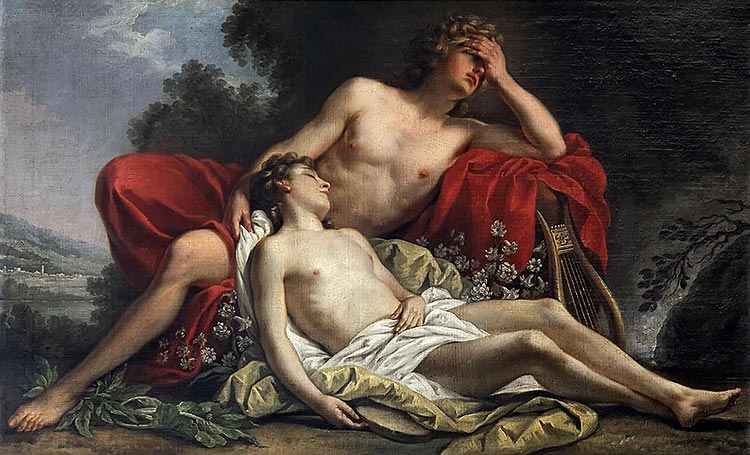

Apollo
The sun god, one of the most important in all literature, was also quite the libertine. Besides dalliances with numerous nymphs, Apollo was also lover to Macedonian Prince Hyakinthos, who died catching a thrown discus, then turned by the god into the hyacinth flower. The Pseudo-Apollodorus also said Apollo had been with Thracian singer Thamyris in the first man-on-man relationship in history. And for those who think same-sex nuptials are a 21st-century invention, Apollo also was in a relationship with Hymen, the god of marriage.
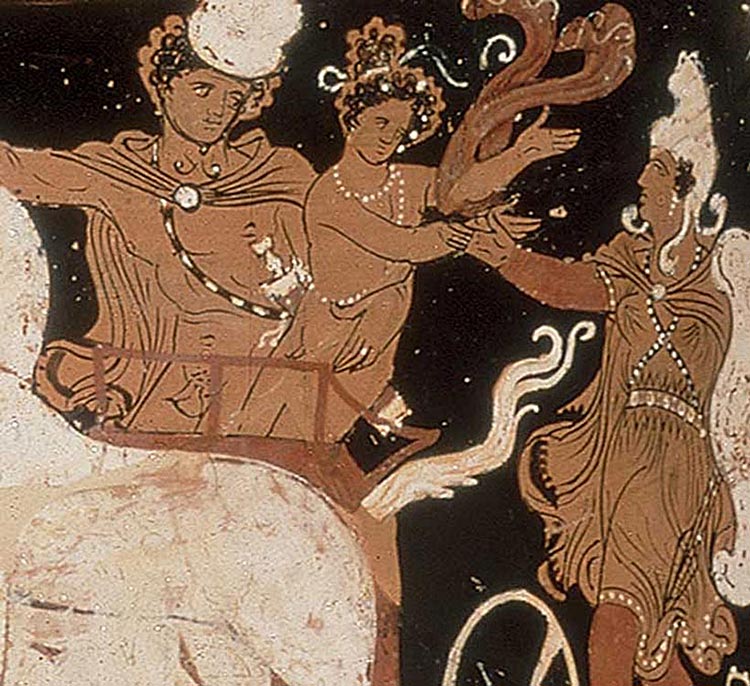

Chrysippus
Euripedes wrote that this divine Peloponnesian hero was on the way to compete in the Nemean Games when his Theban tutor Laius ran off with him and raped him. The incident drew a curse upon the city of Thebes.
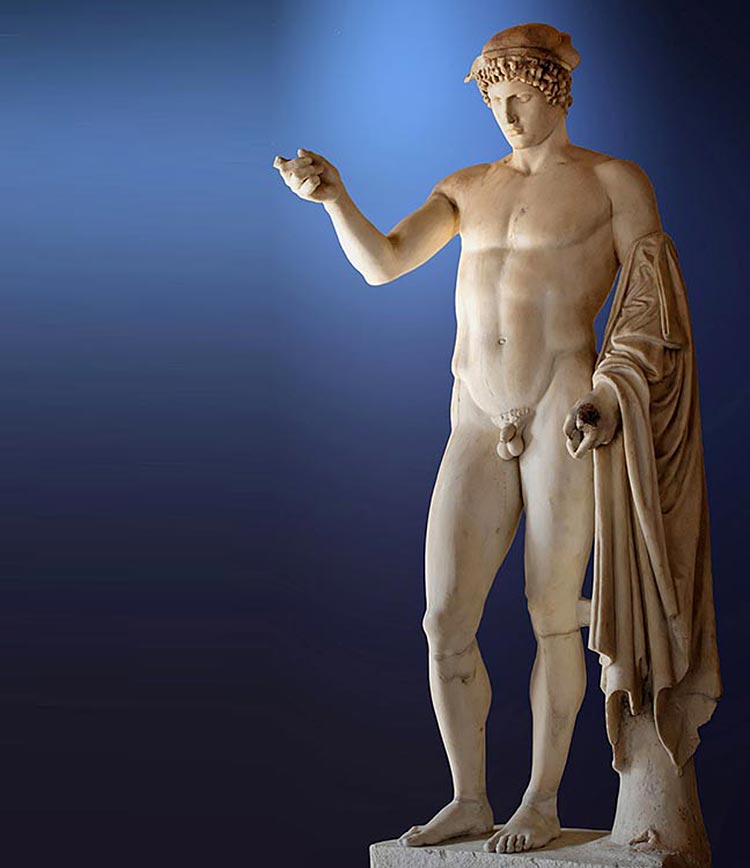

Hermes
The wing-heeled messenger of the gods was said in multiple myths to have male lovers. In a variation of the Hyacinth myth, it was Hermes’ lover Crocus who was killed by a discus thrown by a god before being turned into a flower. Some myths suggest a romantic relationship between Hermes and the hero Perseus. And while some stories list Daphnis, the inventor of pastoral poetry, as the son of Hermes, other sources claim him to be the god of speed’s favorite lover.

Pan
Of course, many mythological texts and artworks connect Daphnis to the satyr Pan, god of music. Pan frequently was depicted in sculpture chasing both women and men around with his always-erect penis and oversized scrotum. Half man. Half goat. Bisexual. Size queen.

Dionysus
Best known as the Greek god of wine, Dionysus was also the god of intersex and transgender people. Male lovers of the god included the satyr Ampelos and the famously handsome Adonis. He also once made a journey to Hades and was guided by the shepherd Prosymnus, who led the way in exchange for the chance to make love to the party god. When Prosymnus died before that deal would be consummated, the god created a wood phallus to ritually fulfill the promise, according to research by a number of Christian historians, including Hyginus and Arnobius.
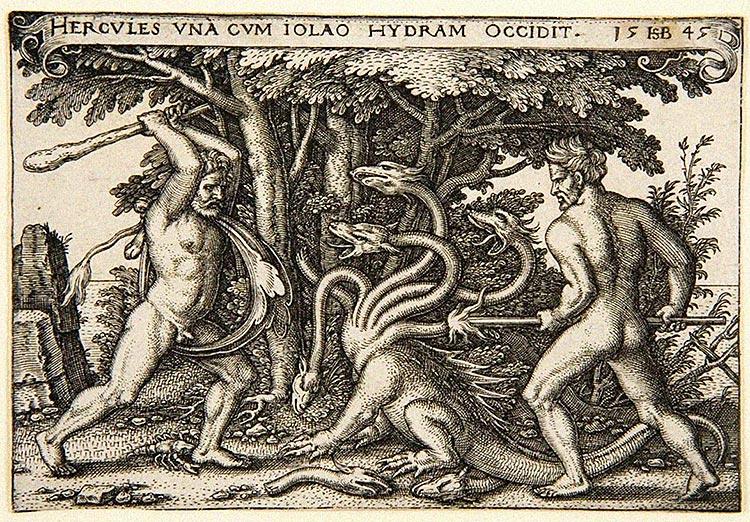

Heracles
The famous hero had a number of male companions through his many trials. Among them: Abderos, who kept the mares of Diomedes for Heracles but was eaten by the beasts; Hylas, Heracles' companion when he sailed on the Argo, who was eventually kidnapped by nymphs in Mysia; and Iolaus, who help cauterize the necks of the hydra when Heracles famously chopped off the beast’s many heads. Indeed, the relationship with Iolaus was enshrined in Thebes, where male couples of the day could be found “exchanging vows and pledges with their beloved at his tomb,” according to historian Louis Crompton.
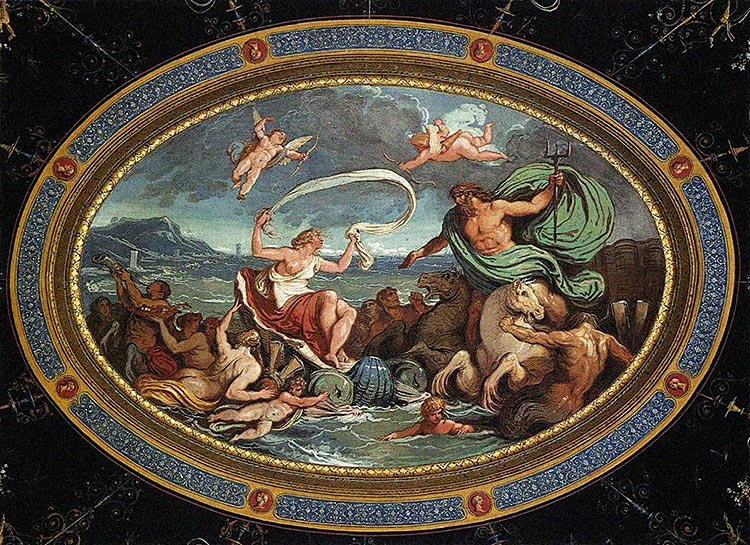
Poseidon
According to Pindar’s First Olympian Ode, Pelops, the king of Pisa, once shared “Aphrodite’s sweet gifts” with the ocean god himself. Pelops for a time was taken to Olympus by Poseidon and trained to drive the divine chariot.

Orpheus
The legendary poet and musician may be best known for the story of his journey to the underworld to retrieve his wife, Eurydice; he failed to do so when he succumbed to temptation and looked at her before both had returned to the world of the living. According to Ovid, he never took another female lover after that — but did love other young men in Thrace. Spurned, Ciconian women would eventually tear Orpheus apart during a Bacchic orgy.
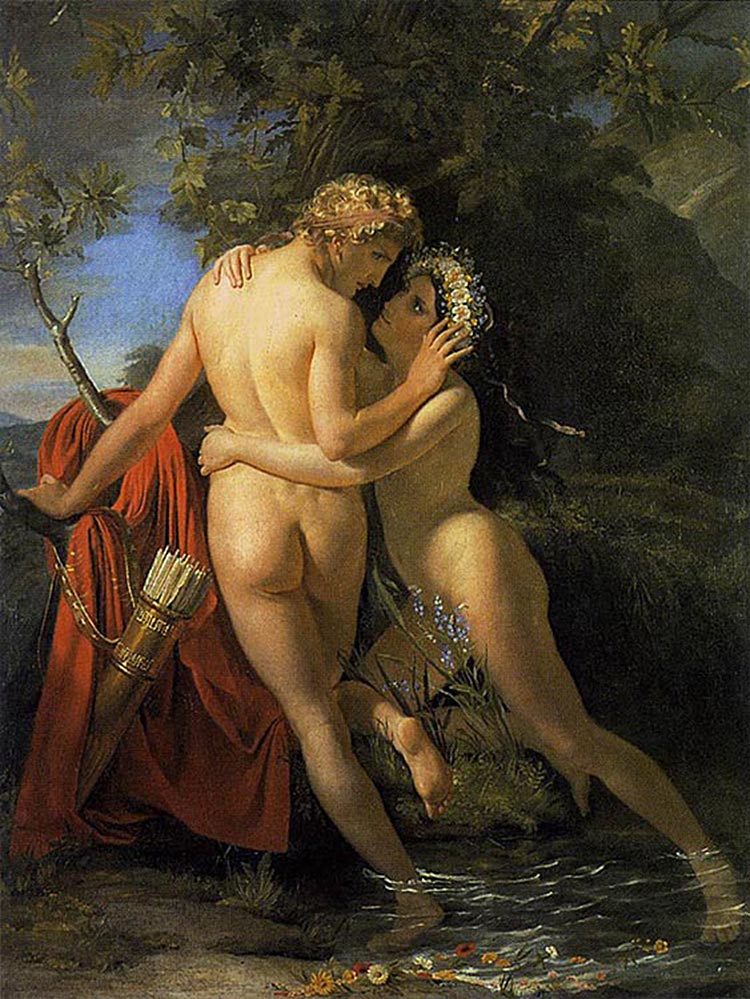

Hermaphroditus
Perhaps the earliest literary reference to an intersex person concerns this child of Hermes and love goddess Aphrodite who as a youth encountered the nymph Salmacis, who attempted to seduce the youth and asked the gods that their forms be permanently joined. The creature of both sexes was frequently depicted in classical art as a figure with womanly breasts and form but with male genitalia.
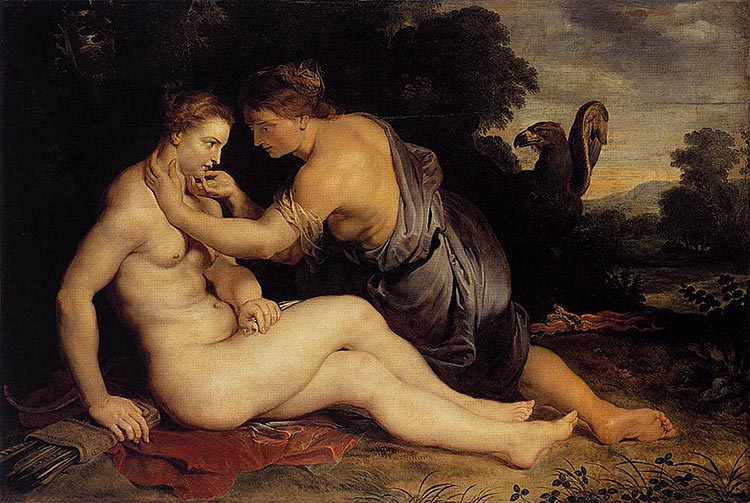
Callisto
This nymph follower of Artemis took a vow to remain a virgin and could not be tempted even by Zeus, at least in male form. But when Zeus disguised himself as Artemis, she was lured into the goddess’s embrace. Hesiod wrote that after this tryst was discovered, Callisto was turned into a bear before she gave birth to son Arcas. Callisto and Arcas were later put in the stars as the constellations Ursa Major and Ursa Minor.
Artemis
Twin sister to Apollo, the goddess was by differing accounts a nearly asexual virgin or a lesbian with many nymph lovers, including Cyrene, Atalanta, and Anticleia as well as moon goddess Dictynna. By some accounts, she was Callisto’s lover before the nymph was raped by Zeus. Researcher Johanna Hypatia-Cybelaia writes that lesbian and gay devotees worshipped her as Artemis Orthia, and that lesbian port Pamphilia referred to the goddess in hymn as Artemis Pergaea.

The Amazons
The original race of warrior women, the Amazons of myth lived in a society free of men, one where the powerful women would only have heterosexual sex once or twice a year — for reproductive purposes only — with male slaves abducted from neighboring villages or taken prisoner during wars, according to Strabo. So what happened the rest of the year? Well, many scholars suggest the idea of a lesbian culture is just modern fantasy, though there is art from the time that depicts Amazonian Queen Penthesilia accepting a love gift from a Thracian huntress.

Teiresias
The blind prophet of Apollo was most famous in Greek myth for being transformed from a man into a woman for seven years. During his female years, Teiresias became a priestess of Hera, married, and even had children, according to Hesiod. Call him mythology’s original transgender person. After the gods changed him back, Zeus asked who enjoyed sex more, men or women. Teiresias revealed the ladies had it roughly 10 times better than the lads. Reporting this earned him a blinding by Hera.

Athena
The goddess of wisdom and patron of Athens was a virgin by nearly every mythological account but did express a romantic attraction to the Attic maiden Myrmex. However, that ended poorly when Myrmex pretended to have invented the plow, one of Athena’s creations, and Athena turned the girl into an ant.

Aphrodite
While the goddess of love is not identified prominently as lesbian herself, the Greek poet Sappho (as in sapphic) of Lesbos (yes, as in lesbian) told many homoerotic tales and named Aphrodite as the greatest patron and ally of lesbians and homosexuals within the Greek pantheon of gods.

Eros
While the best-known myths of Eros depict the son of Aphrodite as a fertility god — the version that proved inspirational to the popularized Roman god Cupid — later Greek myths portrayed Eros as one of several winged erotes, and the one regarded as a protector of homosexual culture, according to research in the scholarly book Among Women: From the Homosocial to the Homoerotic in the Ancient World.

Isis
The Egyptian goddess, also worshipped by Greeks, is known for solving a gender identity issue of yore. Iphis was born female but raised male by his mother, who concealed the truth because her husband wanted a male heir. Ultimately, Iphis fell in love with Ianthe, a woman, and was betrothed to her. Before the wedding, Iphis prayed in the Temple of Isis for a solution, and voila! she became a he.


เทพ 20 องค์ของกรีก ที่เป็น homosexual
Achilles
The Greek hero Achilles was invulnerable excepting his famous weak heel, but a male shieldbearer broke through the warrior’s romantic defenses. While Homer never explicitly states a gay relationship between Achilles and sidekick Patroclus, many scholars read a romantic connection between the two, as only Patroclus ever drew out a compassionate side to the famously arrogant warrior. Patroclus’s death at the hands of Trojan Prince Hector sent Achilles into a rage in which he killed Hector and dragged his body around Troy. Other myths also disclose Achilles was struck by the beauty of Troilus, a Trojan prince.
Zeus
While a famous philanderer who sired countless demigods by every peasant girl in need of an explanation to her parents, Zeus famously selected the young mortal Ganymede to serve as his cupbearer on Mount Olympus. The relationship provided the foundation of the custom of paiderastia, the practice of Greek men at the time maintaining erotic relationships with adolescent boys on the side.
Narcissus
A figure mostly known for his obsessive vanity, this son of a nymph and a river god would spend his last days gazing at his own reflection, but the first man he showed affection for was not himself. A myth traced in origin to the Boeotia region mentions a relationship between Narcissus and the smitten Ameinias, whom Narcissus would eventually grow tired of before sending him a sword as a kiss-off. Ameinias, desperately depressed over the rejection, killed himself.
Apollo
The sun god, one of the most important in all literature, was also quite the libertine. Besides dalliances with numerous nymphs, Apollo was also lover to Macedonian Prince Hyakinthos, who died catching a thrown discus, then turned by the god into the hyacinth flower. The Pseudo-Apollodorus also said Apollo had been with Thracian singer Thamyris in the first man-on-man relationship in history. And for those who think same-sex nuptials are a 21st-century invention, Apollo also was in a relationship with Hymen, the god of marriage.
Chrysippus
Euripedes wrote that this divine Peloponnesian hero was on the way to compete in the Nemean Games when his Theban tutor Laius ran off with him and raped him. The incident drew a curse upon the city of Thebes.
Hermes
The wing-heeled messenger of the gods was said in multiple myths to have male lovers. In a variation of the Hyacinth myth, it was Hermes’ lover Crocus who was killed by a discus thrown by a god before being turned into a flower. Some myths suggest a romantic relationship between Hermes and the hero Perseus. And while some stories list Daphnis, the inventor of pastoral poetry, as the son of Hermes, other sources claim him to be the god of speed’s favorite lover.
Pan
Of course, many mythological texts and artworks connect Daphnis to the satyr Pan, god of music. Pan frequently was depicted in sculpture chasing both women and men around with his always-erect penis and oversized scrotum. Half man. Half goat. Bisexual. Size queen.
Dionysus
Best known as the Greek god of wine, Dionysus was also the god of intersex and transgender people. Male lovers of the god included the satyr Ampelos and the famously handsome Adonis. He also once made a journey to Hades and was guided by the shepherd Prosymnus, who led the way in exchange for the chance to make love to the party god. When Prosymnus died before that deal would be consummated, the god created a wood phallus to ritually fulfill the promise, according to research by a number of Christian historians, including Hyginus and Arnobius.
Heracles
The famous hero had a number of male companions through his many trials. Among them: Abderos, who kept the mares of Diomedes for Heracles but was eaten by the beasts; Hylas, Heracles' companion when he sailed on the Argo, who was eventually kidnapped by nymphs in Mysia; and Iolaus, who help cauterize the necks of the hydra when Heracles famously chopped off the beast’s many heads. Indeed, the relationship with Iolaus was enshrined in Thebes, where male couples of the day could be found “exchanging vows and pledges with their beloved at his tomb,” according to historian Louis Crompton.
Poseidon
According to Pindar’s First Olympian Ode, Pelops, the king of Pisa, once shared “Aphrodite’s sweet gifts” with the ocean god himself. Pelops for a time was taken to Olympus by Poseidon and trained to drive the divine chariot.
Orpheus
The legendary poet and musician may be best known for the story of his journey to the underworld to retrieve his wife, Eurydice; he failed to do so when he succumbed to temptation and looked at her before both had returned to the world of the living. According to Ovid, he never took another female lover after that — but did love other young men in Thrace. Spurned, Ciconian women would eventually tear Orpheus apart during a Bacchic orgy.
Hermaphroditus
Perhaps the earliest literary reference to an intersex person concerns this child of Hermes and love goddess Aphrodite who as a youth encountered the nymph Salmacis, who attempted to seduce the youth and asked the gods that their forms be permanently joined. The creature of both sexes was frequently depicted in classical art as a figure with womanly breasts and form but with male genitalia.
Callisto
This nymph follower of Artemis took a vow to remain a virgin and could not be tempted even by Zeus, at least in male form. But when Zeus disguised himself as Artemis, she was lured into the goddess’s embrace. Hesiod wrote that after this tryst was discovered, Callisto was turned into a bear before she gave birth to son Arcas. Callisto and Arcas were later put in the stars as the constellations Ursa Major and Ursa Minor.
Artemis
Twin sister to Apollo, the goddess was by differing accounts a nearly asexual virgin or a lesbian with many nymph lovers, including Cyrene, Atalanta, and Anticleia as well as moon goddess Dictynna. By some accounts, she was Callisto’s lover before the nymph was raped by Zeus. Researcher Johanna Hypatia-Cybelaia writes that lesbian and gay devotees worshipped her as Artemis Orthia, and that lesbian port Pamphilia referred to the goddess in hymn as Artemis Pergaea.
The Amazons
The original race of warrior women, the Amazons of myth lived in a society free of men, one where the powerful women would only have heterosexual sex once or twice a year — for reproductive purposes only — with male slaves abducted from neighboring villages or taken prisoner during wars, according to Strabo. So what happened the rest of the year? Well, many scholars suggest the idea of a lesbian culture is just modern fantasy, though there is art from the time that depicts Amazonian Queen Penthesilia accepting a love gift from a Thracian huntress.
Teiresias
The blind prophet of Apollo was most famous in Greek myth for being transformed from a man into a woman for seven years. During his female years, Teiresias became a priestess of Hera, married, and even had children, according to Hesiod. Call him mythology’s original transgender person. After the gods changed him back, Zeus asked who enjoyed sex more, men or women. Teiresias revealed the ladies had it roughly 10 times better than the lads. Reporting this earned him a blinding by Hera.
Athena
The goddess of wisdom and patron of Athens was a virgin by nearly every mythological account but did express a romantic attraction to the Attic maiden Myrmex. However, that ended poorly when Myrmex pretended to have invented the plow, one of Athena’s creations, and Athena turned the girl into an ant.
Aphrodite
While the goddess of love is not identified prominently as lesbian herself, the Greek poet Sappho (as in sapphic) of Lesbos (yes, as in lesbian) told many homoerotic tales and named Aphrodite as the greatest patron and ally of lesbians and homosexuals within the Greek pantheon of gods.
Eros
While the best-known myths of Eros depict the son of Aphrodite as a fertility god — the version that proved inspirational to the popularized Roman god Cupid — later Greek myths portrayed Eros as one of several winged erotes, and the one regarded as a protector of homosexual culture, according to research in the scholarly book Among Women: From the Homosocial to the Homoerotic in the Ancient World.
Isis
The Egyptian goddess, also worshipped by Greeks, is known for solving a gender identity issue of yore. Iphis was born female but raised male by his mother, who concealed the truth because her husband wanted a male heir. Ultimately, Iphis fell in love with Ianthe, a woman, and was betrothed to her. Before the wedding, Iphis prayed in the Temple of Isis for a solution, and voila! she became a he.